Difference between revisions of "Daily Practice Routine - Music"
From MusicTechWiki
| Line 49: | Line 49: | ||
{{Description|Tips on developing a practice routine to encourage more comprehensive learning}} | {{Description|Tips on developing a practice routine to encourage more comprehensive learning}} | ||
| − | |||
[[Category:Practice]] | [[Category:Practice]] | ||
| − | |||
[[Category:54A-Music-Theory-Module-04-Content]] | [[Category:54A-Music-Theory-Module-04-Content]] | ||
Revision as of 12:13, 31 May 2022
Practice Log
A practice log charts the time spent at different dimensions of practice. Some students will tend to over-practice within their comfort zone, so explicitly parsing it out like this can encourage more comprehensive learning to occur. Calculating weekly totals gives the student flexibility to focus more on certain dimensions on any given day, rather than forcing just a brief period on every topic every day. They can thus strive to cover all aspects of practice every week. Timing goals (after the slash) can be pre-entered in the Total columns. Below, additional emphasis is prescribed for practicing improvisation (four hours indicated in the bottom Total field, compared to two hours for other dimensions). Sunday has yet to be entered. By keeping a running total, Lillian can tell that she’s generally exceeding her goals, but that she is also coming up short for Ear Training, so she might focus there, to catch up.
You do NOT need to maintain a practice log. This is just as example of what works for some students:
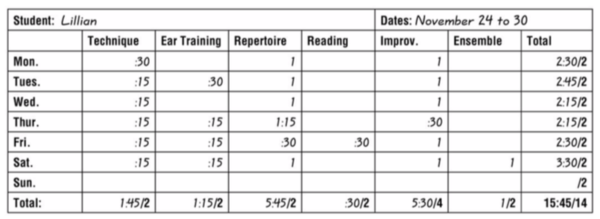
Note: In high school, I practiced 4-6 hours a day. In college, and after college, I practiced 8-14 hours a day (including performing gigs and rehearsals). ~ Bruce Tambling
Practice Routine
Our practice routine should should include a variety of technical and artistic/creative activities.
- Scales
- Modes
- Chords
- Diatonic Chords
- Chord Inversions
- Rhythm Exercises
- Ear Training
- Sight Singing
- Sight Reading - Chords, Rhythms, Melodies
- Improvisation
- Melodic (scales)
- Harmonic (chords)
- Transcribing
- Repertoire
- Learn to play new songs
- Writing music notation
- Be able to write anything you can hear or play
- Must be done by hand first
- Notation software later
- MIDI Programming
- DAW Skills
- Rendering what you hear and play as MIDI data and audio clips in your DAW
- Improvisation
- Listening to Recorded Music
- Ensemble Performance
- Playing in an orchestra
- Jamming in a band
- Jam Tracks
- Music Minus One
- Jam along to records
- Sight read chord charts
- Studying Written Music
- Songwriting and Composition
- Organize improvisations and ideas into arrangements
- Creatively apply what you are learning
- Arranging and Orchestration
- Production
- Develop and produce finished works